Reading Time: 25 Minutes
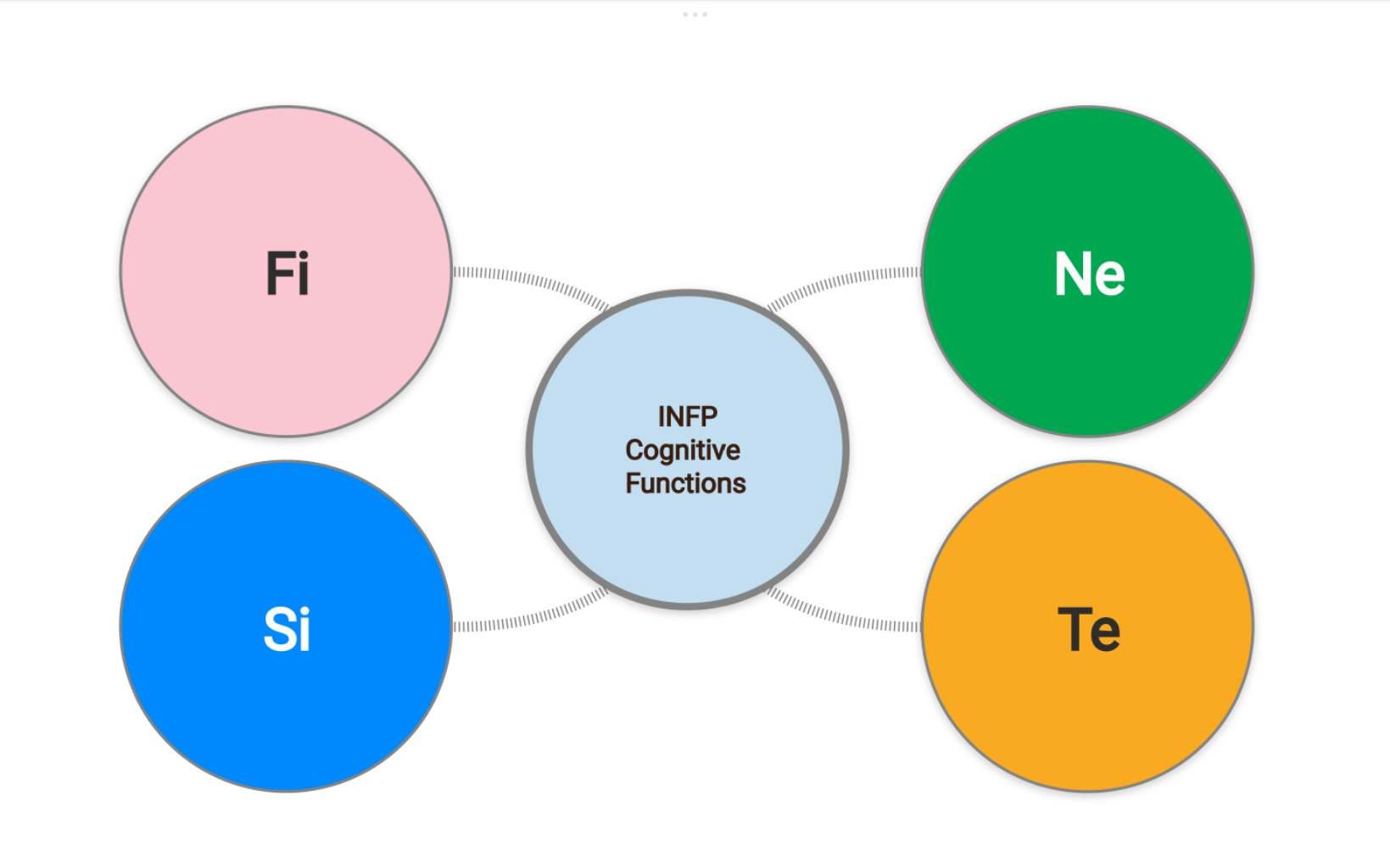
Welcome to the world of INFP Cognitive Functions! If you’ve ever wondered what makes INFPs tick or why they seem like they’re always lost in thought, you’re in the right place. Imagine the INFP brain as a bustling control room, where four unique functions—Introverted Feeling (Fi), Extraverted Intuition (Ne), Introverted Sensing (Si), and Extraverted Thinking (Te)—are working together (and sometimes not).
In this guide, we’ll break down each function, clear up some common myths, compare INFPs to other personality types, and show you how understanding these functions can make life a bit easier for everyone. So, let’s dive in and uncover what makes INFPs tick!
INFP’s Cognitive Function Stack
Understanding the INFP’s cognitive function stack is like peeking under the hood of a car to see what makes it run. Imagine you’ve got four quirky characters in your brain’s control room, each with their own job, and sometimes, they’re not the best at working together. Let’s meet them.
1. Dominant Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
At the helm of the INFP ship is Captain Introverted Feeling (Fi). Fi is like that old-school wise friend who always knows what they stand for and doesn’t budge. This function is all about personal values, morals, and a deep sense of what’s right and wrong. Imagine having a moral compass so strong it could guide you through the foggiest nights.
For INFPs, Fi is their north star. They make decisions based on what feels true to them. They care deeply about authenticity and often find themselves moved by art, music, or a simple act of kindness. But here’s the catch—Fi can be so personal and internal that sometimes INFPs struggle to explain why they feel so strongly about something. It’s like knowing you love a particular flavor of ice cream but not being able to tell others why it’s the best. On a bad day, Fi can get a bit stubborn, making INFPs seem aloof or unyielding.
2. Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Next up, we’ve got Extraverted Intuition (Ne), the idea factory. Ne is like that friend who’s always coming up with new ideas, connecting dots that others didn’t even know existed. INFPs use Ne to explore possibilities, dream up what could be, and get excited about the future.
This function loves to brainstorm and think outside the box. INFPs are often seen daydreaming or hopping from one idea to the next, thanks to Ne. Imagine trying to catch a butterfly with your hands—Ne is that butterfly, always fluttering off to the next flower before you can get a grip on it. While this makes INFPs creative and open-minded, it also means they can sometimes have too many ideas and not enough follow-through. Ne’s challenge? Helping Fi’s deeply held values find a way to turn into action, without getting lost in a sea of possibilities.
3. Tertiary Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
In third place, we’ve got Introverted Sensing (Si). Si is the family historian, always looking back at what’s familiar and comforting. This function helps INFPs remember past experiences in vivid detail, like that time they found the perfect coffee shop or had a great conversation with a friend.
Si is all about traditions and routines. It likes things that feel safe and familiar. For an INFP, this might mean they have a few habits or nostalgic items they hold dear, like re-reading a favorite book or keeping a playlist of songs from their teenage years. Si can be like that friend who always orders the same thing at a restaurant because, hey, if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it. But sometimes, Si can make INFPs resistant to change or too attached to the past, like trying to wear an old pair of shoes that just don’t fit anymore.
4. Inferior Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Bringing up the rear is Extraverted Thinking (Te). Te is like that no-nonsense manager who likes to get things done efficiently and logically. For INFPs, Te is the least developed of the four functions, and it’s often the source of some stress.
Te is all about structure, organization, and making things happen. It’s the function that says, “Enough dreaming, let’s make a plan and do this!” But because it’s in the inferior position, INFPs can struggle with things like setting goals, being assertive, or organizing their lives in a practical way. It’s like having a tool in your toolbox that you know is useful, but you’re not quite sure how to use it without making a mess.
When Te comes out, INFPs might surprise themselves (and others) by suddenly getting super organized or bossy. But more often, they find Te frustrating, like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole. Learning to use Te is part of the INFP’s growth journey, helping them turn their dreams and values into reality.
You Might Like To Read: ISFP Cognitive Functions (Fi,Se,Ni,Te): 4 Functions Explained in Very Simple Manner
Bringing It All Together
So there you have it—the INFP’s cognitive function stack is a mix of deep feelings, endless possibilities, nostalgic memories, and a dash of logic. Each function plays a role in making the INFP who they are: empathetic, creative, and sometimes a bit of a dreamer. It’s all about learning how these functions can work together, even when they don’t always see eye to eye.
How INFPs Use Their Cognitive Functions in Daily Life
Living as an INFP is like juggling four balls, each representing a cognitive function, in the circus of life. Some days, you’re nailing it, and other days, well, let’s just say a few balls hit the ground. Here’s how INFPs use their cognitive functions to navigate the daily grind.
1. Decision-Making Process
When it comes to making decisions, INFPs rely heavily on their trusty captain, Introverted Feeling (Fi). Fi is all about what feels right deep down. So, when an INFP is choosing something important—like a career or even what to have for dinner—they go with what resonates with their personal values. Imagine someone picking a meal because it “feels right for the soul,” not just because it’s tasty.
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) also plays a role by throwing in lots of ideas. “Hey, what if we tried this new dish? Or maybe we could cook at home, or even start a cooking blog!” Ne’s input can make decision-making a bit of an adventure. Sometimes, it’s like shopping with a friend who keeps pulling new items off the shelf, even when you’re ready to check out. But INFPs eventually narrow down their choices based on what Fi approves of, making sure their decisions are authentic and meaningful.
2. Interpersonal Relationships
In relationships, Fi makes INFPs super empathetic. They genuinely care about others and often pick up on the emotional undercurrents in a conversation. They’re the friends who listen to your problems and really get where you’re coming from. However, because Fi is so personal, INFPs might struggle to open up about their own feelings unless they feel completely safe.
Ne adds some spice by encouraging INFPs to explore different perspectives. They’re curious about people’s thoughts, feelings, and ideas, which makes them great conversationalists. Imagine talking to someone who’s always asking questions like, “Have you ever thought about it this way?” or “What if we approached it differently?” That’s Ne at work, keeping things interesting.
Introverted Sensing (Si) helps INFPs remember the little things that matter in relationships, like birthdays, favorite songs, or that one time you laughed until you cried. Si keeps the past alive in a good way, making sure INFPs hold onto those sentimental moments.
On the flip side, Extraverted Thinking (Te) can be a bit of a challenge in relationships. Te is the function that wants to set boundaries and get things done, but for INFPs, it doesn’t come naturally. So, they might struggle with being assertive or organizing their relationships. But when Te does make an appearance, INFPs might suddenly start setting plans or giving advice, surprising everyone around them.
3. Work and Creativity
At work, Fi is the guiding star, pushing INFPs toward careers that align with their values. They thrive in roles where they can be true to themselves and make a positive impact, like counseling, writing, or anything creative. If an INFP doesn’t believe in what they’re doing, it’s like trying to swim upstream—exhausting and ultimately unfulfilling.
Ne fuels their creativity, constantly coming up with new ideas and approaches. INFPs often find themselves daydreaming or thinking of innovative solutions, which can make them great problem solvers. However, Ne can also lead to a bit of chaos, as INFPs might start one project only to jump to another before finishing the first.
Si helps INFPs bring some order to their creative chaos by grounding them in familiar routines and practices. They might have certain rituals, like writing in a favorite notebook or listening to the same playlist while working, that help them focus.
Te, though, is where INFPs might hit a snag. This function is all about structure and efficiency, which doesn’t always come naturally to them. They might struggle with deadlines, organization, or sticking to a strict plan. But when they do engage Te, they can surprise themselves with how much they can accomplish, like suddenly organizing their desk after weeks of clutter.
4. Stress Responses and Function Grip
When the going gets tough, INFPs can fall into what’s known as a “grip” experience, where their inferior function, Te, takes over. Imagine an INFP who’s usually calm and reflective suddenly becoming overly critical or obsessed with getting everything done perfectly. That’s Te in overdrive, and it’s not a fun place to be.
Under stress, Si might also rear its head, making INFPs cling to the past or resist change. They might find themselves longing for “the good old days” or getting stuck in a rut, unable to move forward.
The key for INFPs is to recognize when they’re in a grip and take a step back. Engaging their dominant Fi or auxiliary Ne can help them regain balance, reminding them of what truly matters and opening them up to new possibilities.
Growth and Development for INFPs
Growing as an INFP is like tending a garden. It takes time, patience, and a little bit of effort to see those inner flowers bloom. Here’s how INFPs can cultivate their cognitive functions for personal growth.
1. Enhancing Dominant Fi
To nurture their Fi, INFPs should regularly engage in self-reflection. This could be through journaling, meditation, or simply spending time alone to process their thoughts and feelings. It’s like watering the roots of their values, making sure they stay strong and true.
INFPs should also focus on aligning their actions with their values. This means making decisions that feel authentic, even if they’re not always the easiest choices. It’s like choosing to plant seeds that will grow into the kind of garden they want to see, rather than just scattering whatever comes to hand.
2. Developing Auxiliary Ne
INFPs can grow their Ne by embracing new experiences and ideas. Trying something different, like learning a new skill or exploring a new hobby, can help them expand their horizons. Think of it as letting the garden grow wild for a bit, seeing what blooms when you’re not sticking to the usual paths.
Brainstorming exercises can also help INFPs harness their Ne. They can make lists of ideas, play with “what if” scenarios, or even engage in creative writing. The key is to let Ne roam free without worrying too much about where it’s going—sometimes, the best ideas come from unexpected places.
3. Strengthening Tertiary Si
To balance their Ne, INFPs should develop their Si by establishing some routines and traditions. This doesn’t mean getting stuck in a rut, but rather finding comfort in certain habits that bring a sense of stability. It’s like having a favorite corner of the garden where everything feels just right.
INFPs can also benefit from organizing their memories in a positive way. Reflecting on past experiences and learning from them, rather than dwelling on what went wrong, can help Si become a source of strength rather than a crutch.
4. Managing Inferior Te
Finally, INFPs should work on embracing their Te to bring some structure into their lives. This might mean setting small, manageable goals or learning to be more assertive when necessary. It’s like putting up a trellis in the garden—giving those wild, creative ideas something to climb on.
Te can be a challenge, but with practice, INFPs can learn to use it without feeling overwhelmed. They might start with simple tasks like organizing their workspace or setting a daily schedule, gradually building up to more complex planning.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About INFP Cognitive Functions
When it comes to INFPs, people often have a lot of ideas that, quite frankly, miss the mark. These misconceptions can make INFPs feel like they’re walking around with a label stuck to their forehead that says, “Handle with Care: Fragile Dreamer Inside.” Let’s clear up some of these myths and set the record straight.
1. Myth: INFPs Are Overly Emotional
One of the biggest misconceptions is that INFPs are like emotional sponges, soaking up every little feeling until they’re dripping with sentiment. Sure, INFPs have deep emotions, thanks to their dominant Introverted Feeling (Fi), but they’re not just a bundle of nerves waiting to cry at the sight of a cute puppy.
In reality, INFPs feel things deeply, but they also have a strong sense of control over those feelings. They don’t just wear their hearts on their sleeves—they tuck them safely inside, only pulling them out for people and situations that really matter. Think of it this way: they’re more like emotional ninjas, quietly feeling things without making a big show of it.
2. Myth: INFPs Are Impractical Dreamers
Another common myth is that INFPs are so caught up in their daydreams that they can’t handle real life. People sometimes think INFPs are the type to forget to pay the bills because they were too busy writing poetry in a meadow.
While it’s true that INFPs love to dream and explore possibilities (thanks to their Extraverted Intuition, or Ne), they’re not completely out of touch with reality. They know how to take care of the practical stuff when they need to—they just prefer to focus on things that feed their soul rather than their bank account. So, yes, they might daydream about traveling the world, but they also know how to book the plane tickets and pack a suitcase when the time comes.
3. Myth: INFPs Are Indecisive
Some folks think INFPs can’t make a decision to save their lives. They imagine them as the person in the grocery store aisle, staring at two different brands of cereal for an hour because they just can’t choose.
The truth is, INFPs do take their time with decisions, but that’s because they want to make sure they’re making the right one. Their Fi function demands that their choices align with their values, and Ne offers up so many options that it can be a bit overwhelming. But once they’ve made up their mind, they’re pretty firm about it. So, they might take a while to decide what to do for dinner, but when they do, you can bet it’s a meal they’re excited about.
Comparing INFP Cognitive Functions with Other Types
Now, let’s take a look at how INFPs stack up against a few other personality types. It’s like comparing apples to oranges—each is unique, but understanding the differences helps you appreciate what makes INFPs special.
1. INFP vs. INFJ
Both INFPs and INFJs are known for being deep, introspective, and caring, but they go about it in different ways. The key difference is in their feeling functions: INFPs use Introverted Feeling (Fi), while INFJs use Extraverted Feeling (Fe).
INFPs make decisions based on their own internal values, like an artist painting from the heart. They focus on staying true to themselves, even if it means going against the crowd. INFJs, on the other hand, are more attuned to the emotions and needs of others. They’re like the social glue that holds a group together, always trying to keep harmony.
Another big difference is in their perceiving functions: INFPs use Extraverted Intuition (Ne), while INFJs use Introverted Intuition (Ni). INFPs are all about exploring possibilities and coming up with new ideas. They’re like idea factories, constantly churning out creative concepts. INFJs, with their Ni, are more focused on long-term visions and patterns. They’re the big-picture thinkers who can see where things are headed.
2. INFP vs. INTP
INFPs and INTPs might seem similar at first because they both love to think deeply, but they’re actually quite different in how they process the world. INFPs lead with Fi, making them driven by their values and emotions. They’re the kind of people who follow their hearts, even if it leads them off the beaten path.
INTPs, on the other hand, lead with Introverted Thinking (Ti). They’re logic-driven and love to analyze everything down to the tiniest detail. Imagine a scientist carefully dissecting a theory to see how it works—that’s Ti in action. INFPs might wonder if something feels right, while INTPs are more likely to ask if it makes logical sense.
When it comes to intuition, both types use Extraverted Intuition (Ne), which makes them open-minded and curious. However, INFPs tend to explore ideas that align with their values, while INTPs are more interested in understanding how things work.
3. INFP vs. ENFP
INFPs and ENFPs share a lot in common—they’re both idealistic, creative, and love exploring new possibilities. The big difference? INFPs are introverts, while ENFPs are extroverts.
INFPs recharge by spending time alone, reflecting on their values and ideas. They’re like a phone that needs to be plugged in to a quiet corner to recharge. ENFPs, on the other hand, get their energy from being around people. They’re more like solar panels, soaking up energy from the sun (or in this case, social interactions).
Both types use Fi and Ne, but because ENFPs are extroverted, they tend to be more outgoing and spontaneous. INFPs, while also open to new experiences, are a bit more reserved and thoughtful in how they approach the world.
Practical Applications of Understanding INFP Cognitive Functions
So, why does all this matter? Understanding INFP cognitive functions isn’t just for fun—it’s like having a manual for how to get the most out of life as an INFP. Here’s how you can put this knowledge to good use.
1. Improving Relationships
Knowing about your cognitive functions can help you better understand yourself and others. For instance, when you realize that your Fi makes you care deeply about certain values, you can communicate that to others in your life. Instead of just getting frustrated when someone doesn’t understand why something matters to you, you can explain it clearly and help them see where you’re coming from.
It also helps you understand why you might feel overwhelmed in certain situations, like when Te takes over under stress. Instead of beating yourself up, you can recognize what’s happening and take steps to calm down and return to your more natural Fi-Ne way of thinking.
2. Enhancing Personal Growth and Self-Care
Understanding your cognitive functions can also guide your personal growth. If you know that Te is your weaker function, you can work on developing it without expecting perfection. Maybe you start by setting small goals, like organizing your workspace or planning your week ahead of time. Over time, you’ll find it easier to bring structure to your life without feeling like you’re betraying your true self.
And let’s not forget self-care. Knowing that you need alone time to recharge means you can give yourself permission to say “no” to social events when you need to. You’ll understand that taking care of your Fi and Si needs—like spending time reflecting or enjoying a comforting routine—helps you stay balanced and happy.
3. Leveraging Cognitive Functions for Career Success
In your career, understanding your cognitive functions can help you choose a path that aligns with your strengths. If you know that Fi and Ne drive you, you might seek out jobs that allow you to be creative, help others, or work on projects that you’re passionate about. You’ll also be more aware of the challenges you might face—like needing to develop your Te to handle deadlines and organization.
But it’s not just about choosing the right job. Understanding your cognitive functions can also help you excel in whatever role you’re in. You’ll know how to leverage your strengths, like using Ne to come up with innovative solutions, while also working on your weaknesses, like improving your time management.
4. Navigating Challenges by Understanding Function Dynamics
Finally, when challenges arise, understanding your cognitive functions can help you navigate them more effectively. If you find yourself in a stressful situation, knowing that you might fall into a Te grip can help you take steps to calm down and regain control. You can use strategies like focusing on your Fi values or engaging in a familiar Si routine to ground yourself.
In summary, understanding your INFP cognitive functions is like having a map to guide you through life’s ups and downs. It helps you make better decisions, improve your relationships, grow as a person, and succeed in your career. Plus, it’s always good to know why you’re wired the way you are—it’s like finding out you’ve got a secret superpower, just waiting to be unleashed.
Conclusion On INFP Cognitive Functions
So there you have it—INFP Cognitive Functions in a nutshell. From understanding their deep-seated values to exploring endless possibilities and managing stress, these functions shape how INFPs experience the world. Knowing about these functions can help you better understand yourself or the INFPs in your life, making interactions smoother and growth easier. Whether you’re an INFP or just curious about what’s going on in that wonderfully complex mind, this guide should give you a clearer picture of how those inner gears are turning. So, keep this handy, and you’ll be navigating the world of INFPs like a pro!
If you like the post, then please don’t forget to share with your friends.
Some Of The Previous Posts